WBE: Which method is fastest?
Topics Featured
Sample processing for measuring SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater involves sample preparation, sample concentration, RNA extraction and RNA measurement methods. Methods selected at each step must be tailored for use with wastewater, which is a chemically and biologically complex and variable mixture. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends evaluating the performance of these wastewater sample processing procedures using appropriate laboratory controls.

Concentration approaches evaluated to date that yield adequate recovery for SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater include:
- Ultrafiltration
- Filtration through an electronegative membrane with sample pre-treatment by addition of MgCl2 or acidification
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation
- Skimmed milk flocculation
- Ultracentrifugation
The CDC says to consider the following factors when selecting a virus concentration method:
- Sample type: For untreated wastewater samples, several filtration and precipitation methods, listed above, are available. For primary sludge samples, centrifugation is the most effective way to concentrate solids.
- Sample volume: Large untreated wastewater sample volumes may require dividing the sample prior to membrane filtration (due to slow filtration rate) or PEG precipitation (due to centrifuge volume constraints). Sample volumes greater than 5 L may require pre-concentration by methods designed to concentrate a large volume, such as large cartridge ultrafiltration.
- Potential supply chain issues: Methods that require commercial filtration products, such as membrane filters or ultrafiltration cartridges, may be more sensitive to supply chain issues than other methods.
- Sample processing time: Concentration method selection will be constrained by method processing time and availability of laboratory personnel. Membrane filtration of turbid wastewater samples may take several hours.
- Availability of laboratory equipment: Centrifuge volumes and force capacity, as well as availability of membrane filtration units, will also constrain method selection.

Nucleic acid extraction and purification is an essential step in isolating SARS-CoV-2 RNA from the sewage mixture. Sewage is a complex mixture with materials known to interfere with molecular viral quantification methods, so consider the following when selecting an extraction method:
- Select an extraction protocol designed to produce highly purified nucleic acid extracts from environmental samples. Commercial kits are available for environmental sample extraction.
- Use an extraction kit or a protocol that is designed specifically to purify RNA and includes RNase denaturants prior to lysis.
- Avoid degradation of extracted RNA due to multiple freeze-thaw cycles by aliquoting extracts into separate tubes and storing them at -70 °C or below.
Nanotrap® Microbiome Particles from Streck provide a simple and rapid approach for concentration of microbes from various sample types. They utilize affinity capture and enrichment technology to bind low abundance targets. The particles concentrate microbes from 24 wastewater samples in 40 minutes, faster than other automated methods such as PEG precipitation or ultracentrifugation.
Are you searching for a fast WBE program? We put two methods in the ring for the lab match of the century!
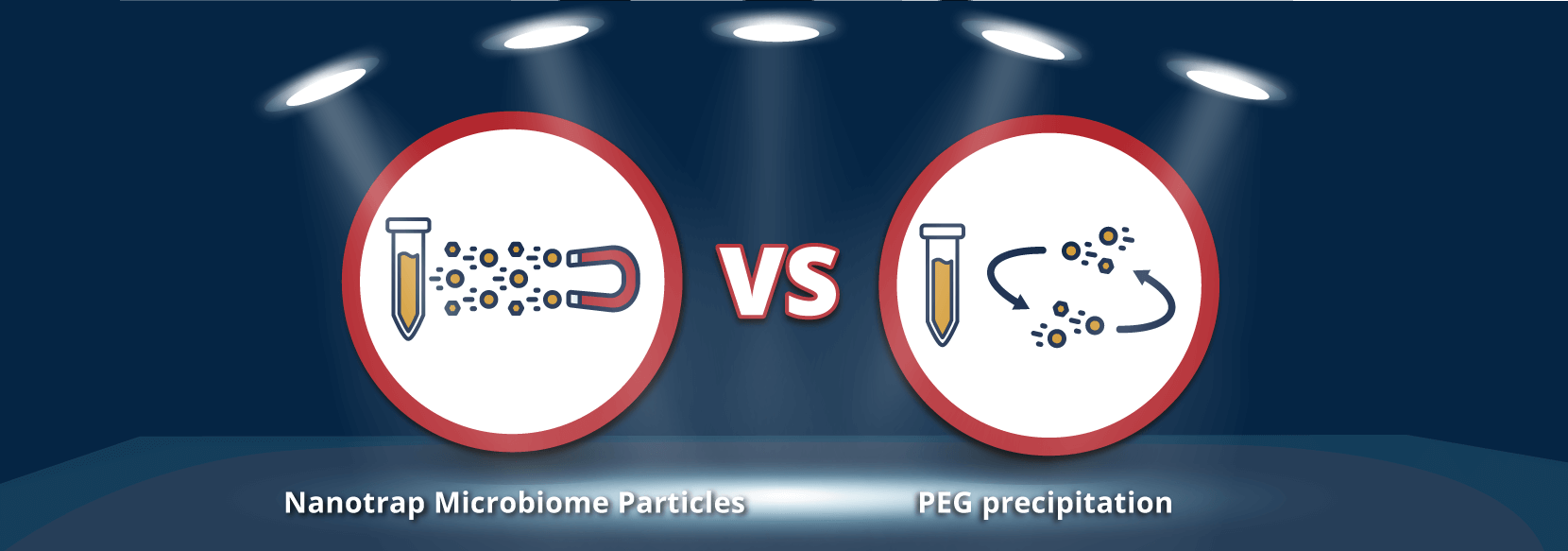
In one corner we have the swift newcomer Nanotrap® Microbiome Particles — and in the other, heavy-hitting, slower-than-slow veteran PEG precipitation. They will battle for the title of fastest and most efficient method to capture and concentrate microorganisms from your complex wastewater-based epidemiology samples.
When the bell sounds, Nanotrap Microbiome Particles land time saving blows in your lab with lightning-fast performance. The particles streamline your sample processing protocol — capture and concentrate 24 samples in 42.5 minutes (manual). Old-timer PEG precipitation can take up to 21 hours!


The clear winner of this smackdown in the lab is Nanotrap Microbiome Particles!
Click here to view The WBE Smackdown comparison of the Nanotrap Microbiome Particles procedures vs. PEG Precipitation.
Nanotrap® Microbiome Particles (For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.), distributed by Streck, offer a simple and rapid approach for concentration of SARS-Co-V-2 from large volume wastewater samples.

How can wastewater predict the future?

