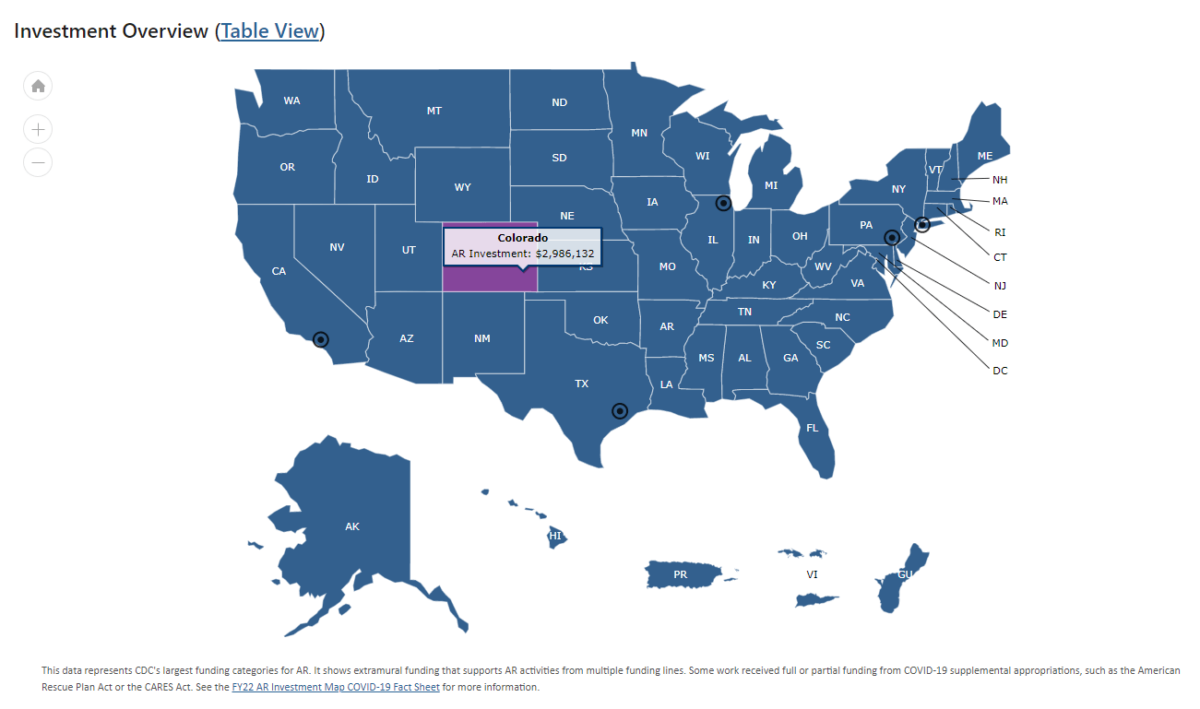
CDC updates AR investment map
Topics Featured
AR occurs when germs are unresponsive to drugs and other chemotherapies designed to kill them. AR threatens to return the world to a time when even simple infections could be fatal. By tracking and monitoring the instances of AR at the local and state level, public health authorities and clinicians can make more informed decisions on the treatment options for various AR-containing microbes.
The CDC mandates both phenotypic determination and genotypic confirmation of AR from clinical isolates submitted to ARLN laboratories. Phenotypic determination of AR is through Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of cultures exposed to antimicrobial agents. Genotypic confirmation is through quantitative or qPCR, digital PCR or Next Generation Sequencing (NGS).
The AR data is sent to the CDC from the ARLN labs and used to provide a comprehensive epidemiological picture of antimicrobial resistant microbes in the United States.
Nearly half of ARLN labs, including the CDC, use the Streck ARM-D® Kits for genetic confirmation of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. The ARM-D Kits are a comprehensive and easy-to-use qPCR-based assay that detects over 1,000 genetic variants of 18 unique AR families, including the families considered urgent threats by the CDC: NDM, KPC, VIM, IMP and OXA. The ARM-D Kits are compatible with most of the commonly used Real-Time PCR instruments and thus do not require any additional analyzer purchases. The ARM-D Kits were found to be 100% concordant with NGS results (CDC Poster, ASM-Microbe – 2018).
How can wastewater predict the future?