Clear advantage of glass BCTs
Topics Featured
When choosing between glass or plastic blood collection tubes designed to maintain the cell-free DNA population, there is an often overlooked aspect worth consideration: the effect tube material has on preservative shelf life and blood draw volume.
Blood collection tubes (BCTs) are a vital component of modern medicine. They are generally made of either non-reactive glass or polyethylene terephthalate (PET). There is a perception in the field that plastic is superior to glass when targeting cell-free DNA (cfDNA). PET is becoming the material of choice for BCTs due to low cost, clarity and un-breakability. However, Streck recently performed a study that showed Streck glass Cell-Free DNA BCT® blood collection tubes have many benefits for cell-free DNA preservation.
Limitations of plastic blood collection tubes
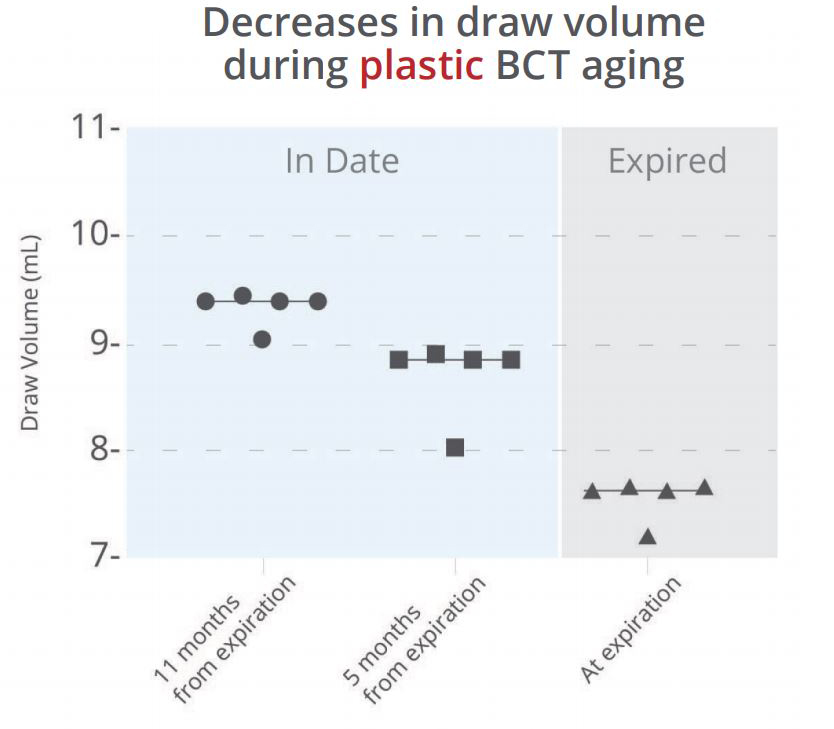
A key limitation with using PET plastic blood collection tubes is that they have poor vacuum retention and high water permeability. In our study, we collected water into five tubes for each of three lots of common plastic blood collection tubes of various ages. There was a substantial change in the draw volume as the tubes aged, even while still in date (Figure 1a). This decrease in draw volume will reduce the amount of blood drawn into the tube, reducing the amount of recoverable plasma, which may affect downstream assays or cause additional difficulty for rare target detection.
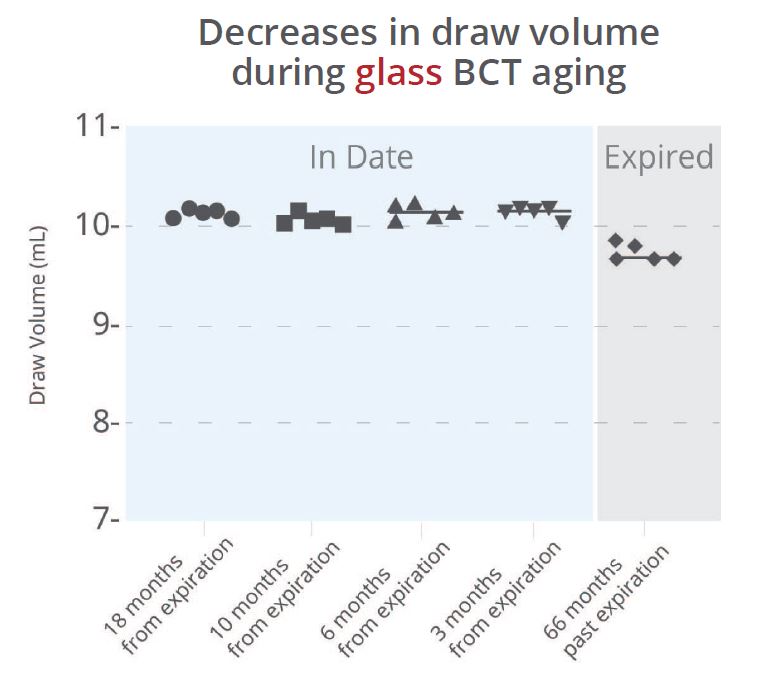
In contrast, the drawn amount of water in glass Streck Cell-Free DNA BCTs was maintained and vacuum was retained throughout dating and for years after expiration (Figure 1b).
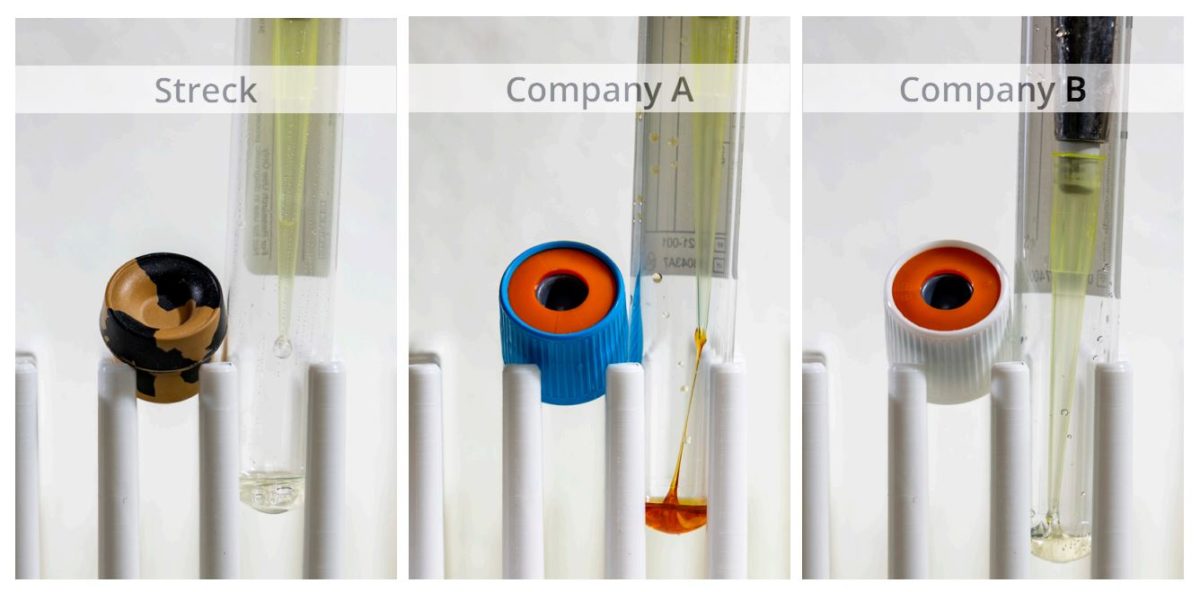
Most stabilizing reagents are a liquid at the time of manufacturing. However, when a liquid reagent is placed into a plastic tube it loses moisture and turns into a viscous gel as the product ages. Because of the water retention properties of glass, Streck’s Cell-Free DNA BCT reagent remains a liquid even years past expiration (Figure 2).
Poor vacuum retention and loss of moisture shortens the shelf life of PET plastic BCTs and can lead to inconsistent results as the product ages. Glass BCTs maintain vacuum and have better moisture retention, leading to a long shelf life. Streck Cell-Free DNA BCT, provides the best shelf life, performance near expiration and sample draw volume when stabilization is required.

Cell-Free DNA BCT is a blood collection tube which limits cellular degradation and resultant release of genetic material into the plasma, keeping the cfDNA free from contamination during storage, shipping, or batching.
Cell Free-DNA BCT is for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. A CE version of these tubes is also available. Cell-Free DNA BCT CE is for Export Only. Not for sale in the U.S. This is also licensed for sale in Canada.


FDA clearance brings liquid biopsy into a new era