Why does stabilization matter?
Topics Featured
Human blood is packed with genetic information found in circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and cell-free RNA (RNA). Liquid biopsy takes advantage of this, using a simple blood draw to gain knowledge about a patient, from predisposition to cancer to whether a traumatic brain injury has occurred. Because several diseases are associated with increased circulating cfDNA and cfRNA, it is paramount that analysis of samples reflects concentrations of these analytes at draw time. This leaves laboratories with two options: either analyze the samples immediately or use a stabilization tube to maintain nucleic acid concentrations.
By stabilizing blood samples, clinicians can ensure that the data collected during liquid biopsy is an accurate reflection of what is in the patient’s blood. Without stabilization, samples can degrade over time. This is due to the breakdown of white and red blood cells, which results in the release of genomic DNA (gDNA), extracellular vesicles (EVs) and EV-associated cfRNA. Sample deterioration may lead to non-specific increases in these analytes, thus confounding analysis of the original sample.
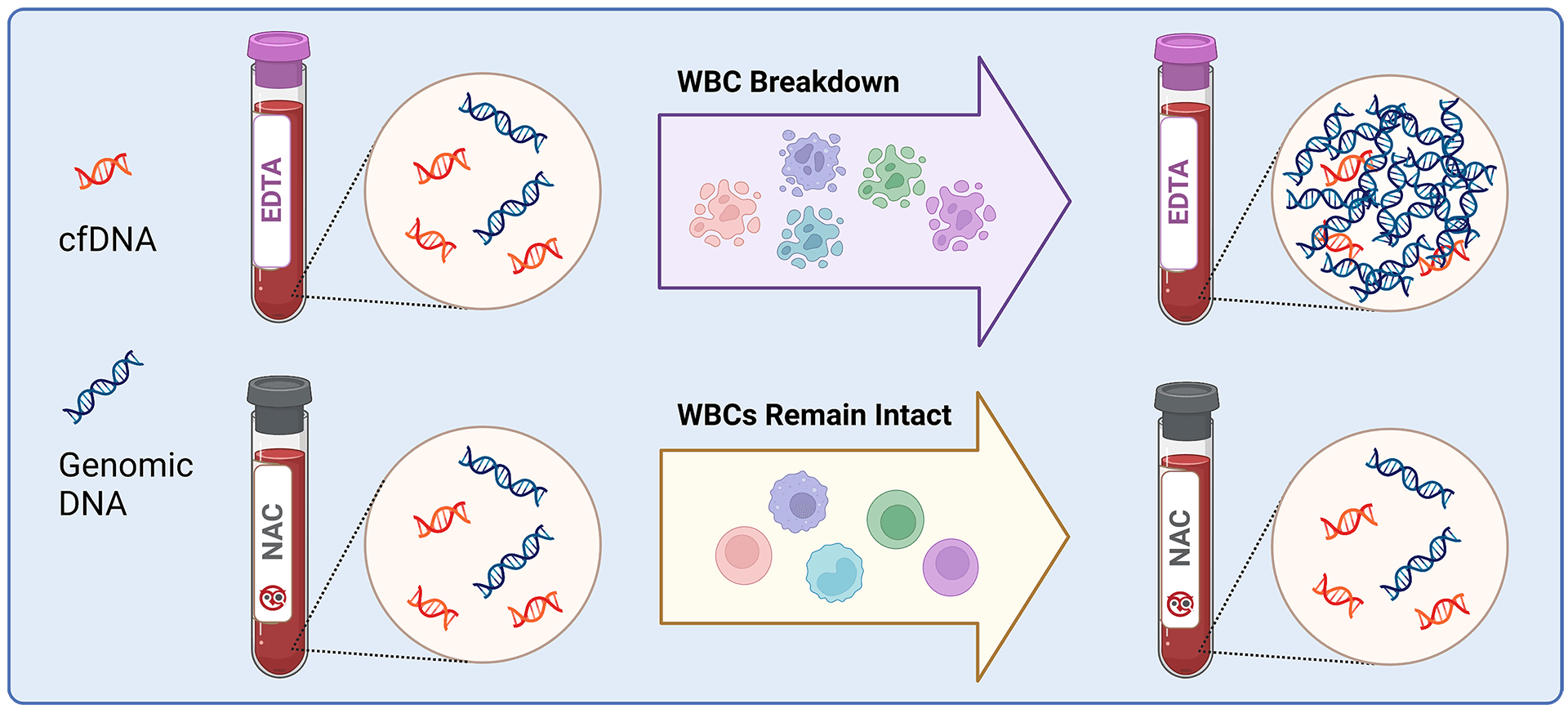
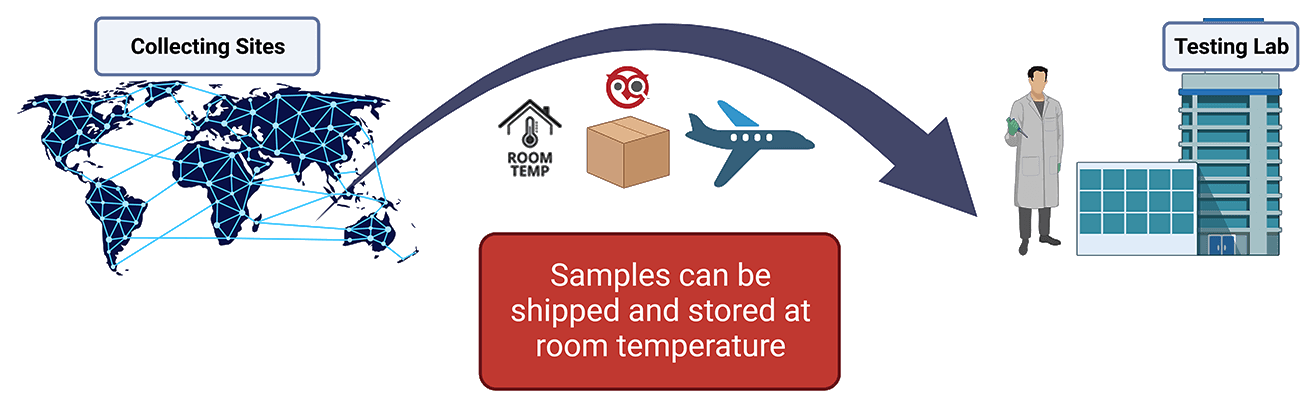
While traditional means of sample storage, such as EDTA tubes, briefly maintain sample integrity, they do not support long-term room temperature storage. As a result, samples that are collected into EDTA must be analyzed soon after collection. Stabilization tubes, like Nucleic Acid BCT™ from Streck, increase the time between collection and analysis by maintaining analyte levels to draw-time concentrations. With Nucleic Acid BCT, draw-time cfDNA, cfRNA and EV particle concentrations are stabilized for up to 7 days at room temperature, allowing for focus to shift from worry about sample degradation to analysis of data.
The benefits of stabilization extend beyond accurate diagnoses. Incorporating stabilization tubes, such as Nucleic Acid BCT, into testing workflows eliminates the need for cold storage, reducing shipping and handling costs. This is ideal for groups who send samples to off-site laboratories, as it extends storage time without compromising analysis. Stabilization also promotes laboratory efficiency: Samples collected into Nucleic Acid BCT can be run once a week as a batch, whereas samples collected into EDTA, or other traditional collection tubes, require immediate attention. By maintaining sample integrity, laboratories can minimize inaccurate analysis, reduce costs and maximize efficiency.
With Streck’s patented portfolio of stabilization products, laboratories can feel confident in their findings without the pressure and cost of immediate analysis of samples. We don’t stop at blood, either— our Streck® Urine Preserve and Streck Cell Preservative® enable scientists to mitigate and limit pre-analytical variation in urine and body fluid samples, easing handling concerns and allowing for room temperature storage, cold chain-free shipping and batch processing.
Nucleic Acid BCT and Streck Urine Preserve are for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.

Stable samples ready for any research mission.
Download our guide to explore blood collection tubes and stabilization reagents specific to your target analytes.


The Benefits of Glass BCTs

